Acupuncture Meridians
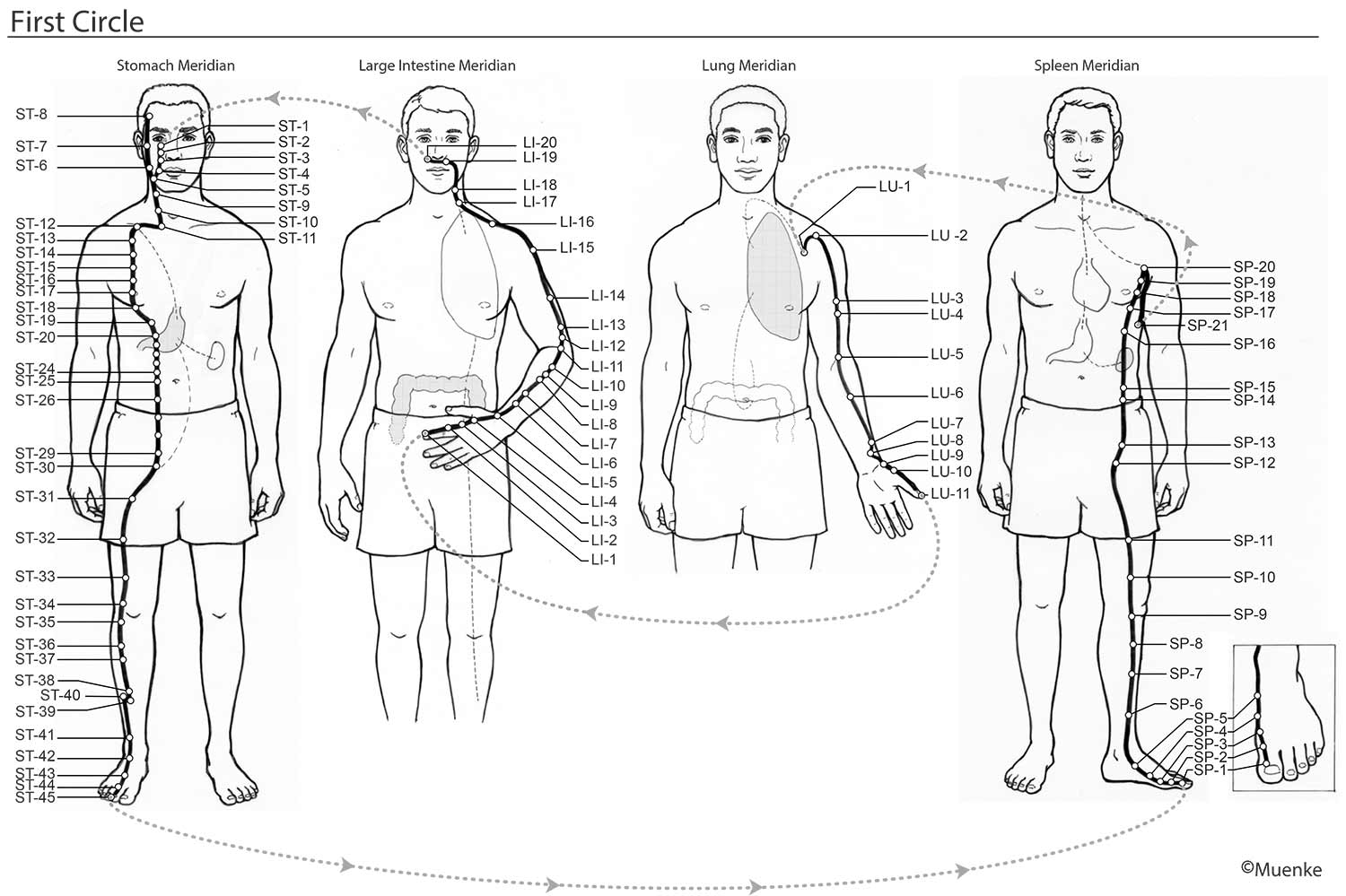
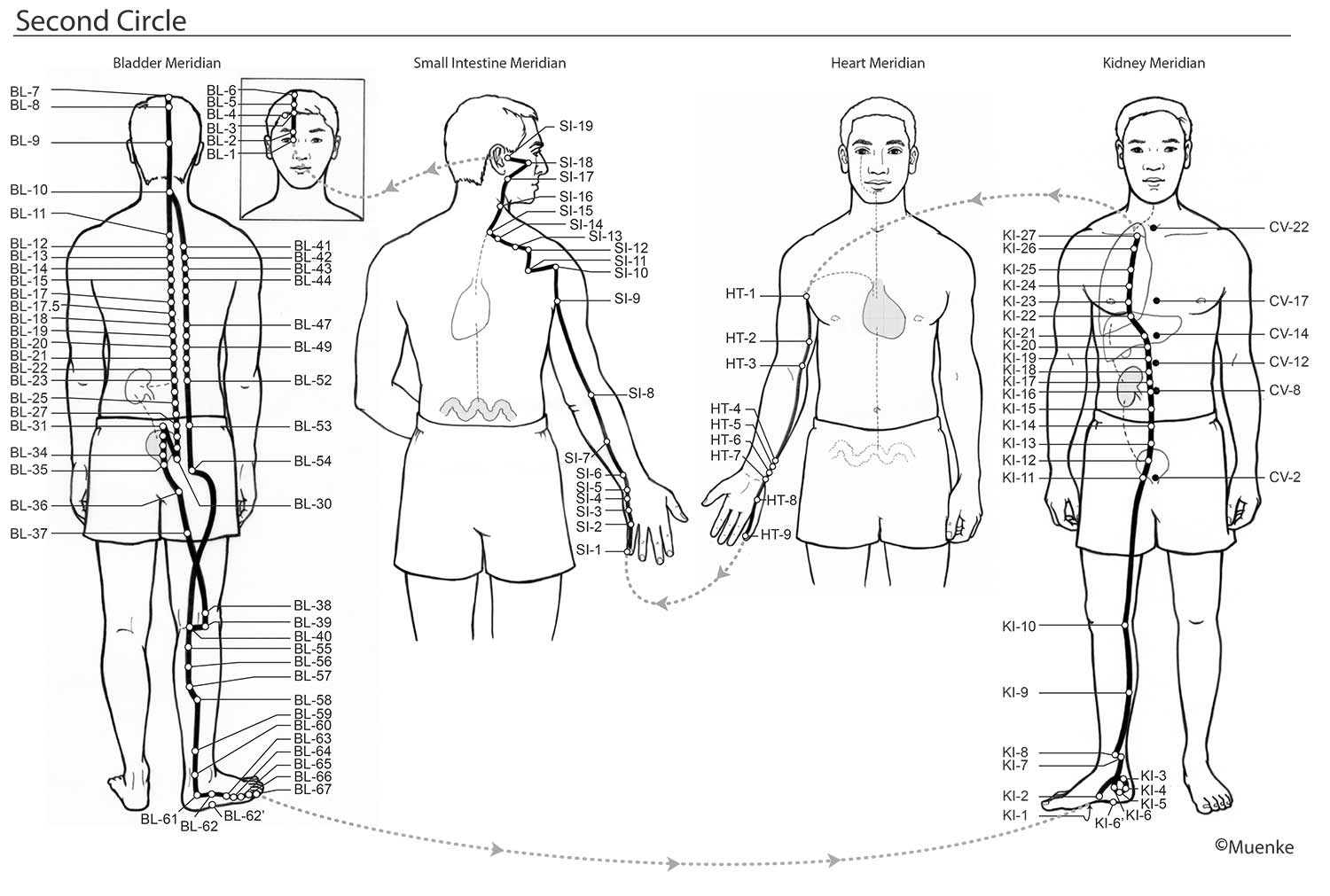
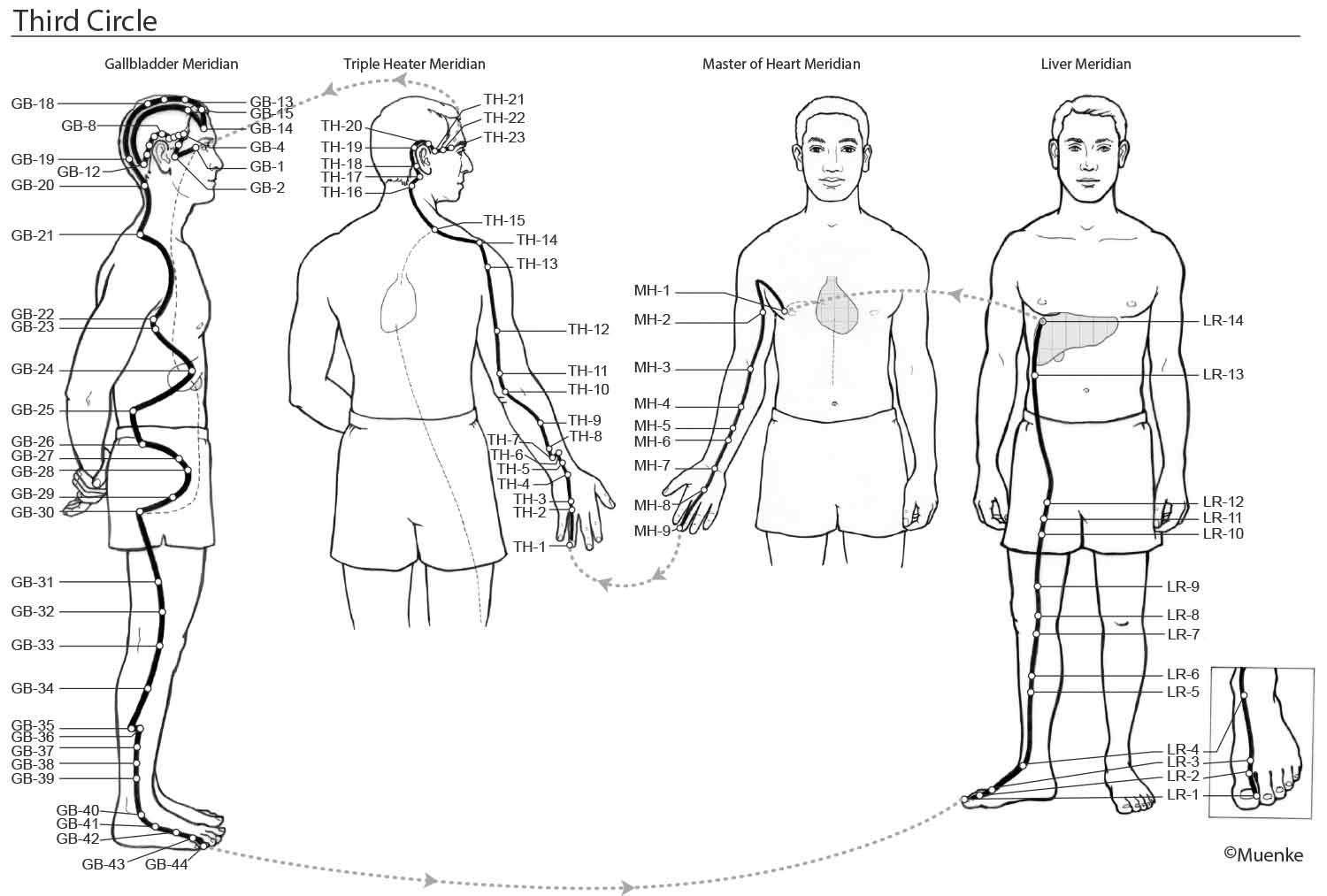
Meridians are “energy highways” of the body. They are connected with each other and their associated organs that they are named after (see Circles 1, 2, and 3). At specific surface points along these meridians, so-called acupuncture or acupressure points Qi can be manipulated to increase the flow of energy along these meridians and to their organs. The goal of Traditional Chinese Medicine is not just absence of disease, but a healthy mind, body and spirit, achieved through the balanced, smooth and unhindered flow of energy along the meridians.
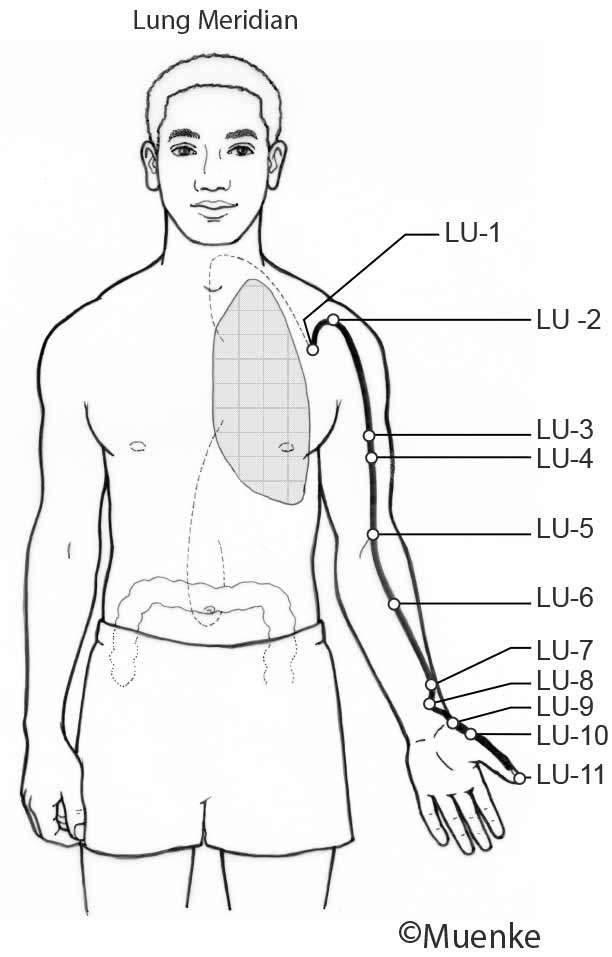
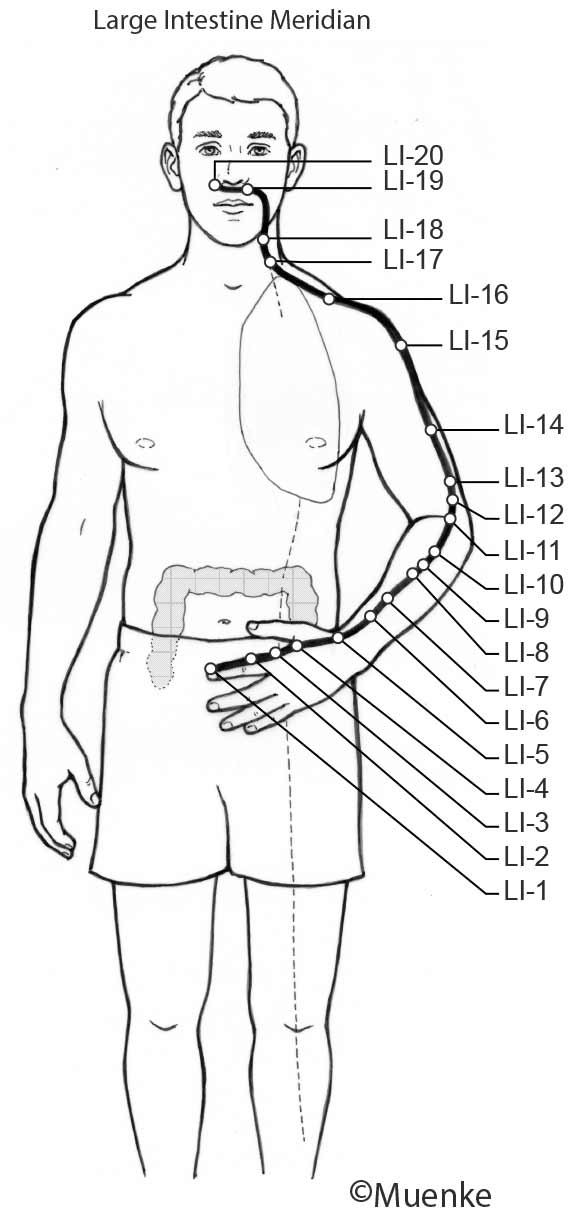
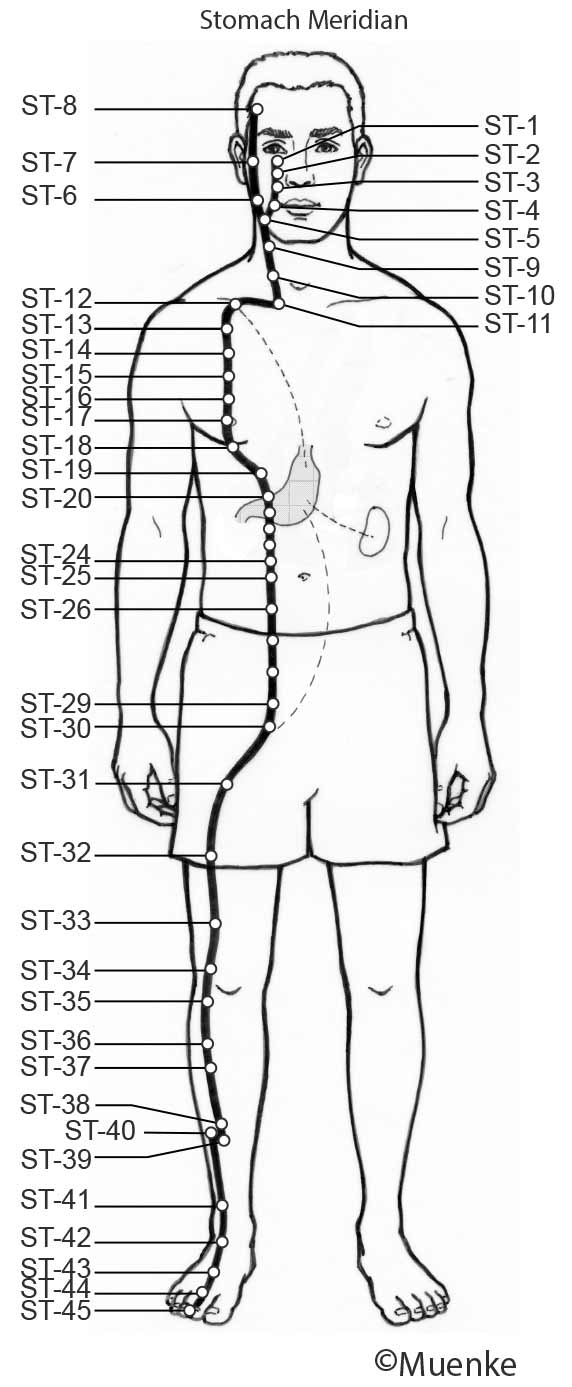
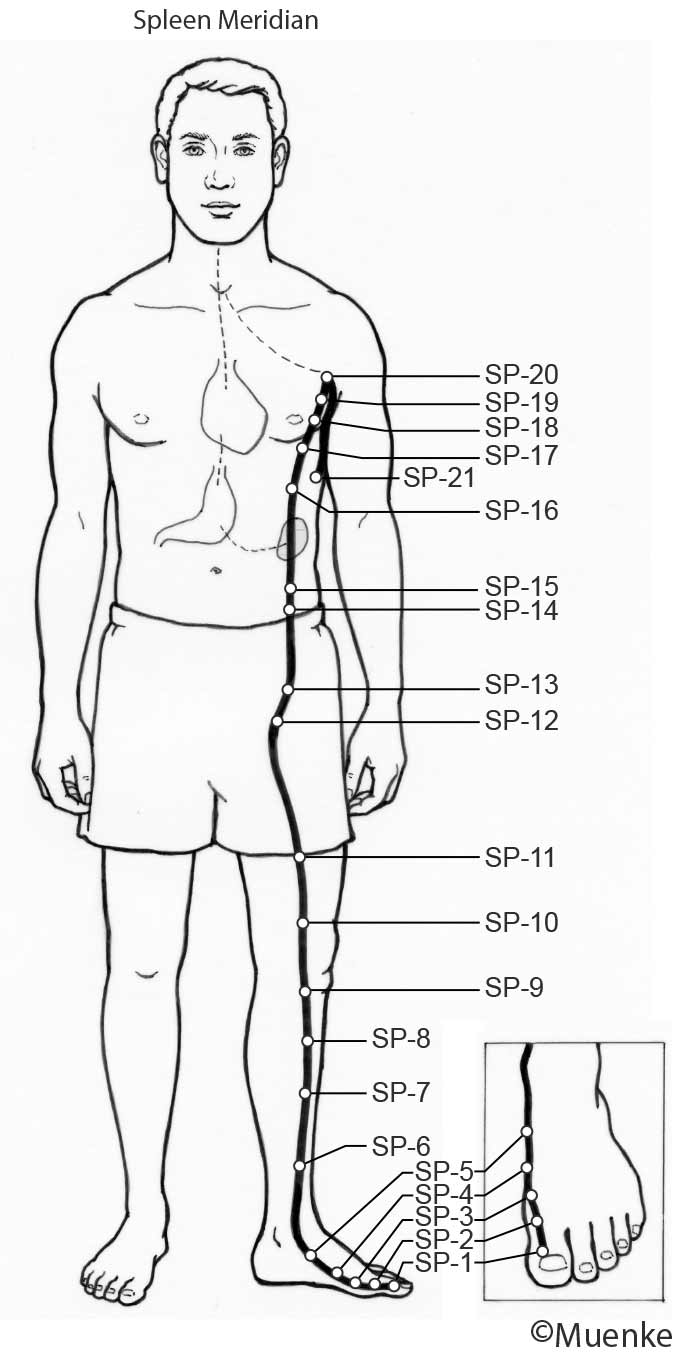
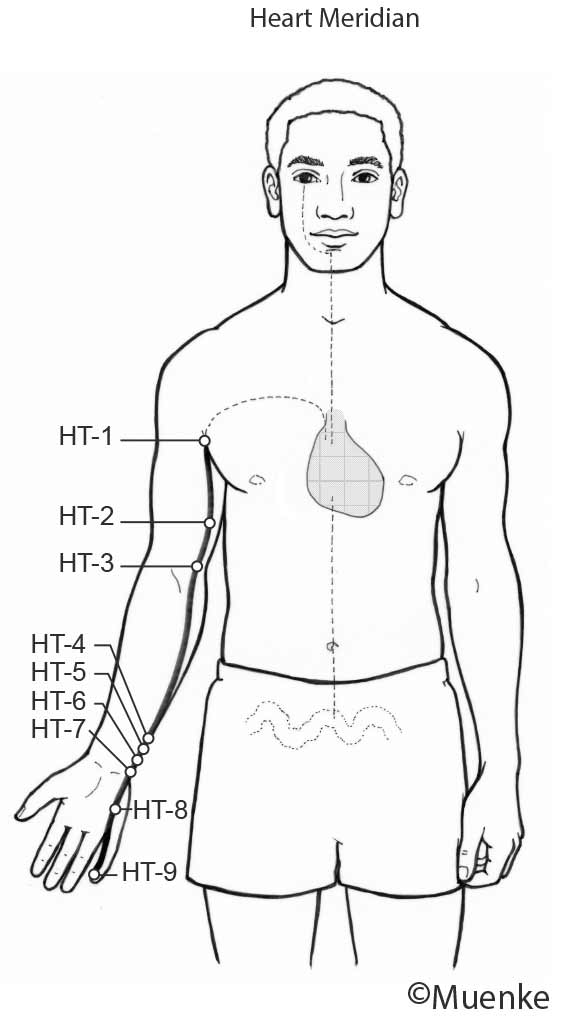
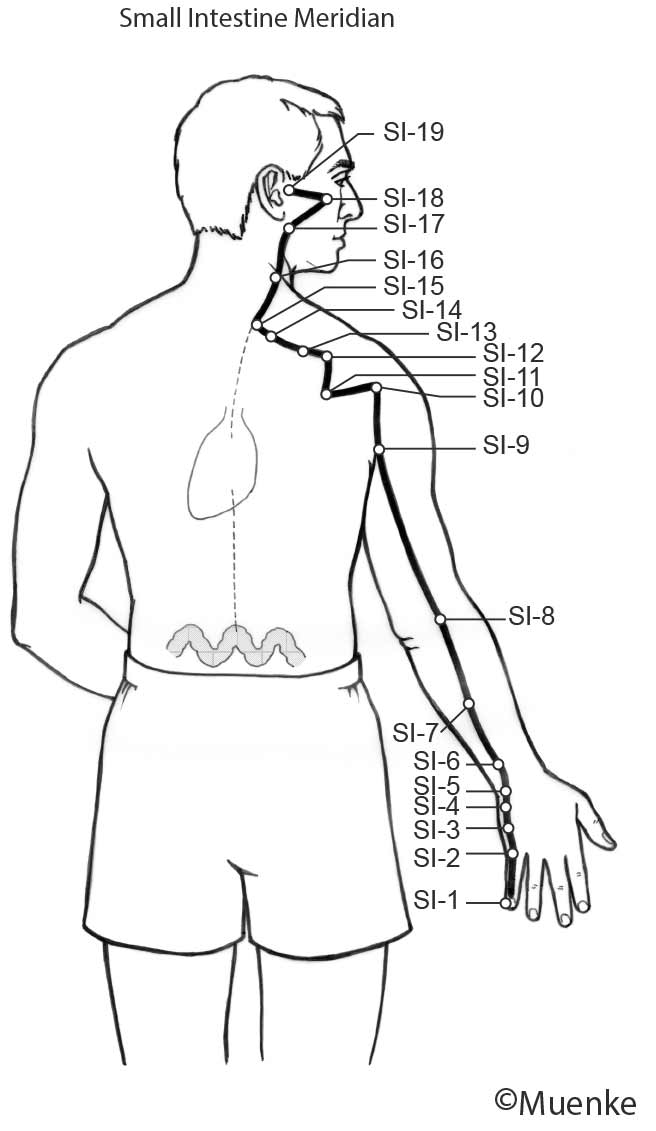
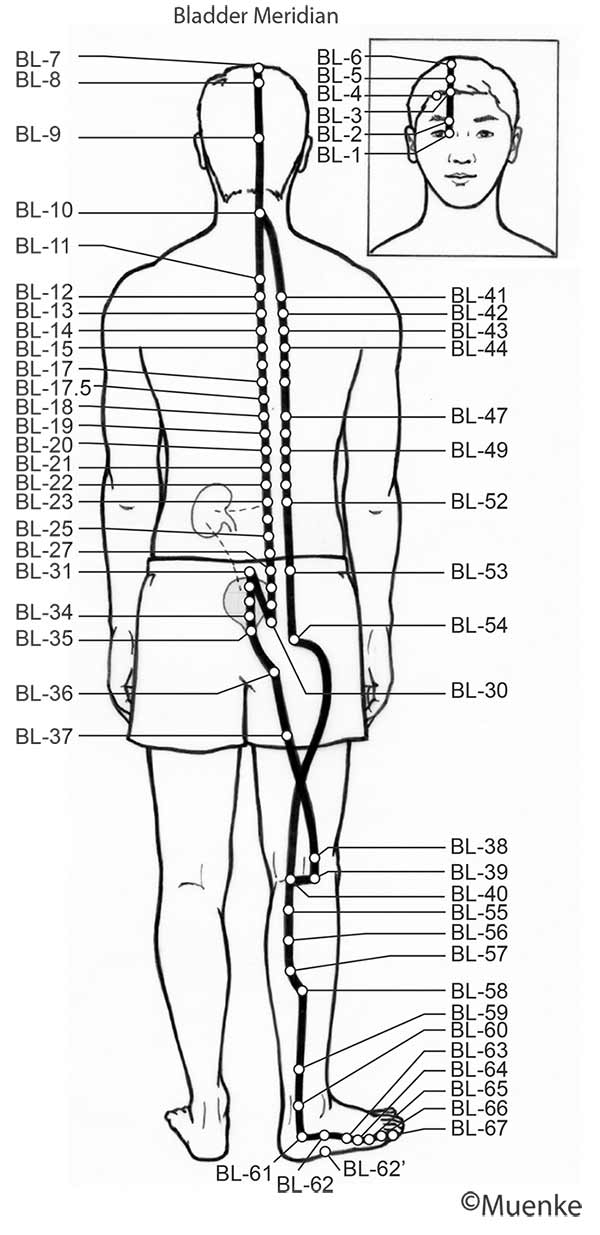
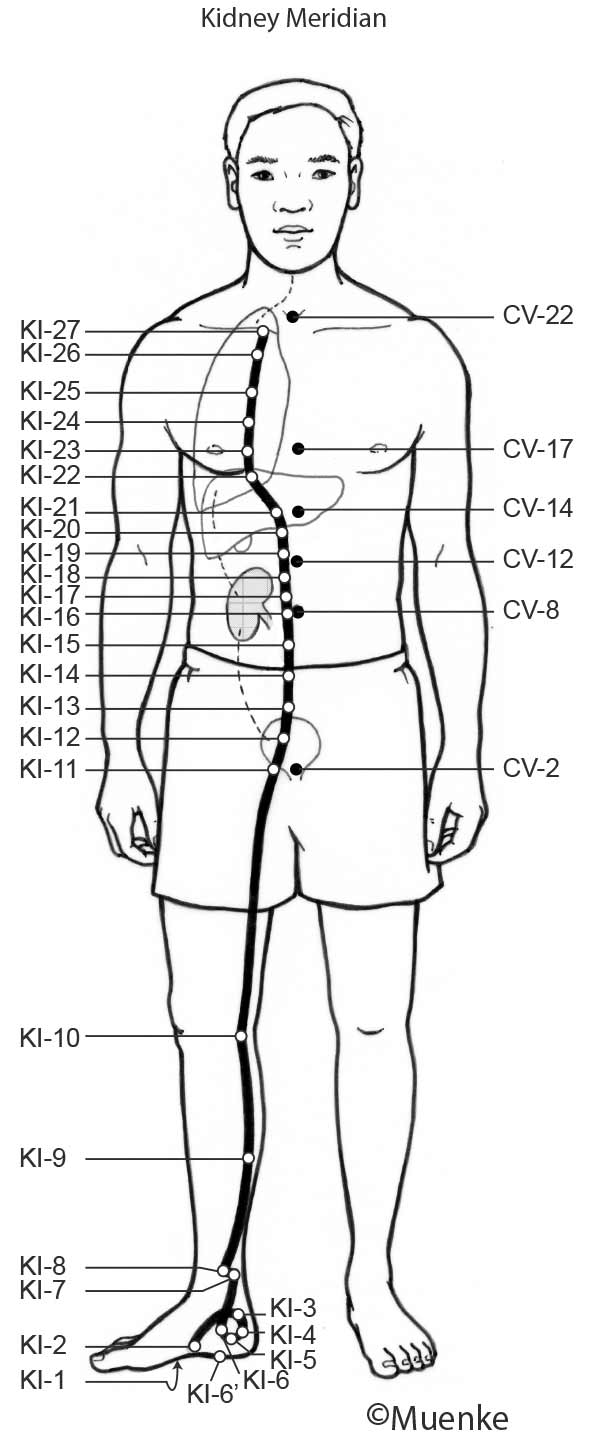
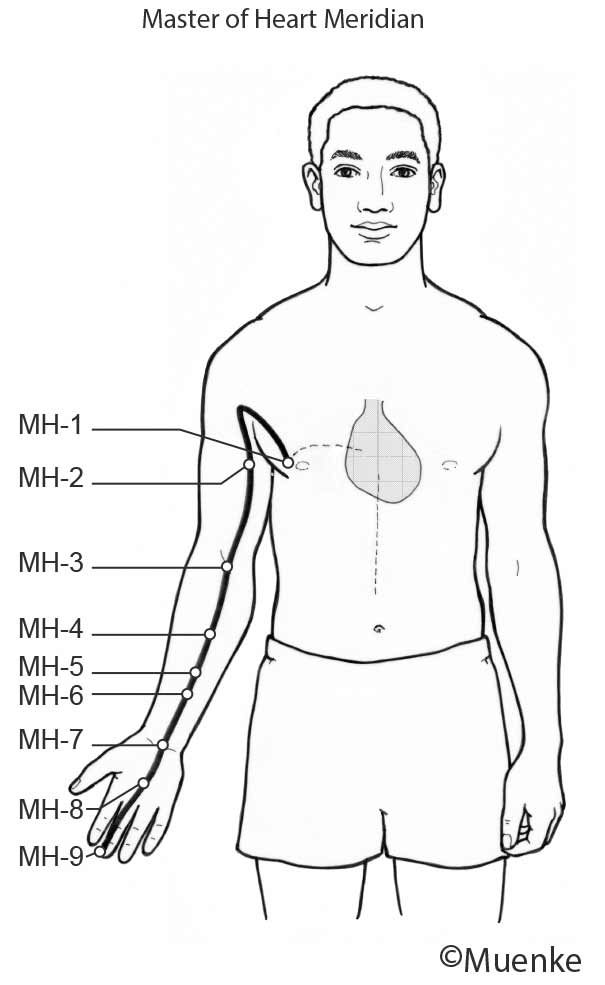
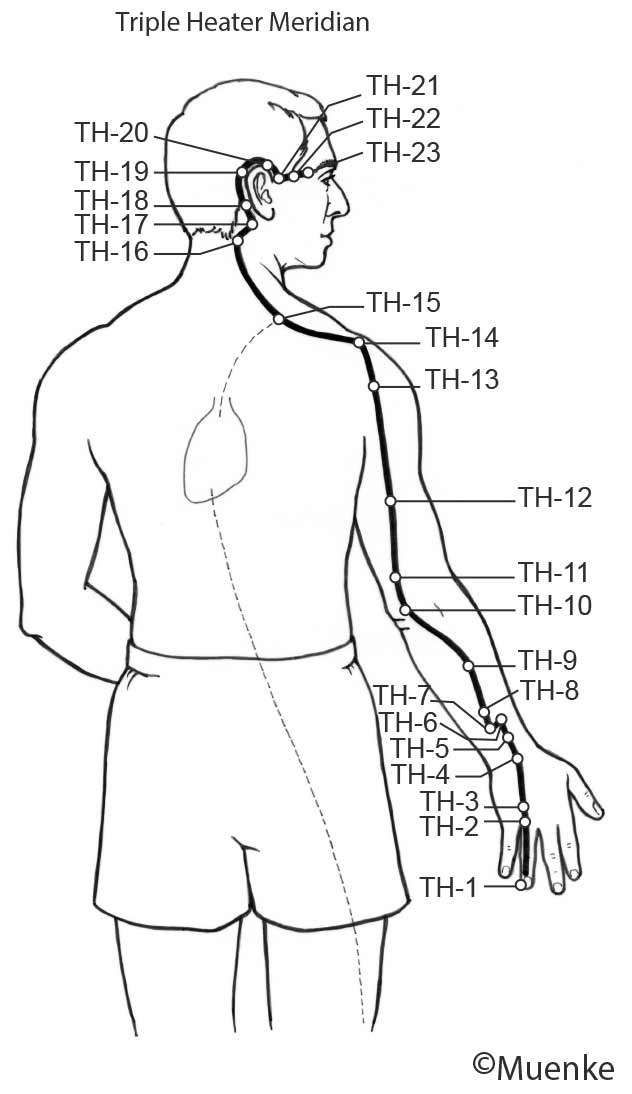
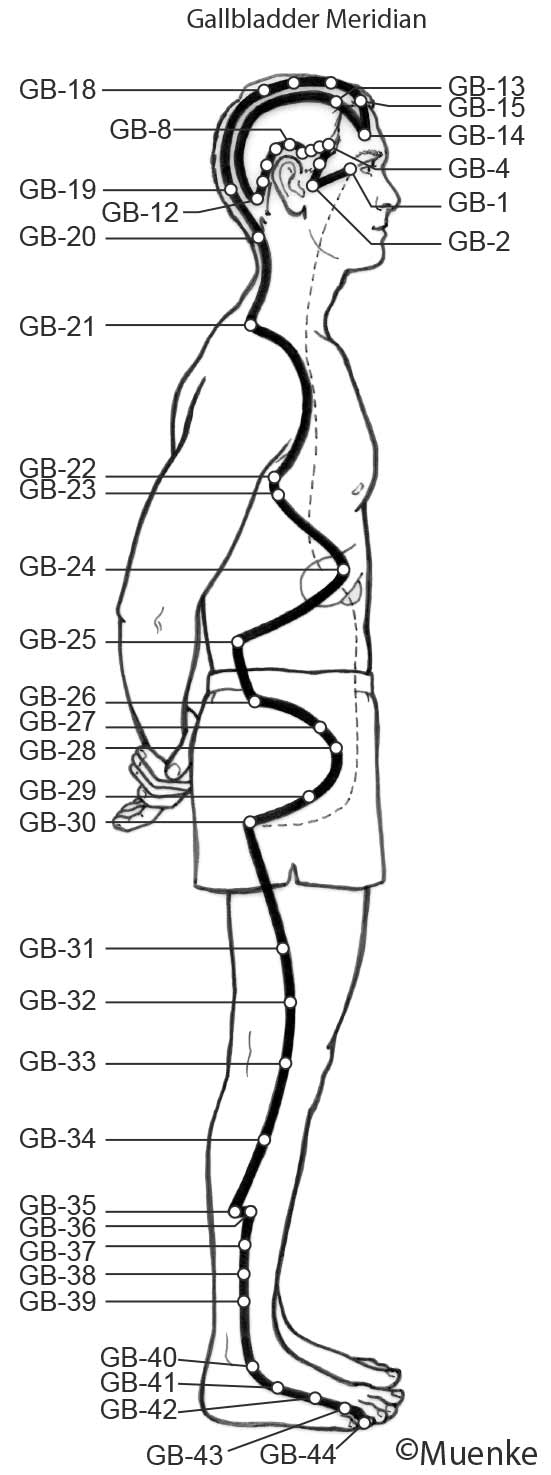
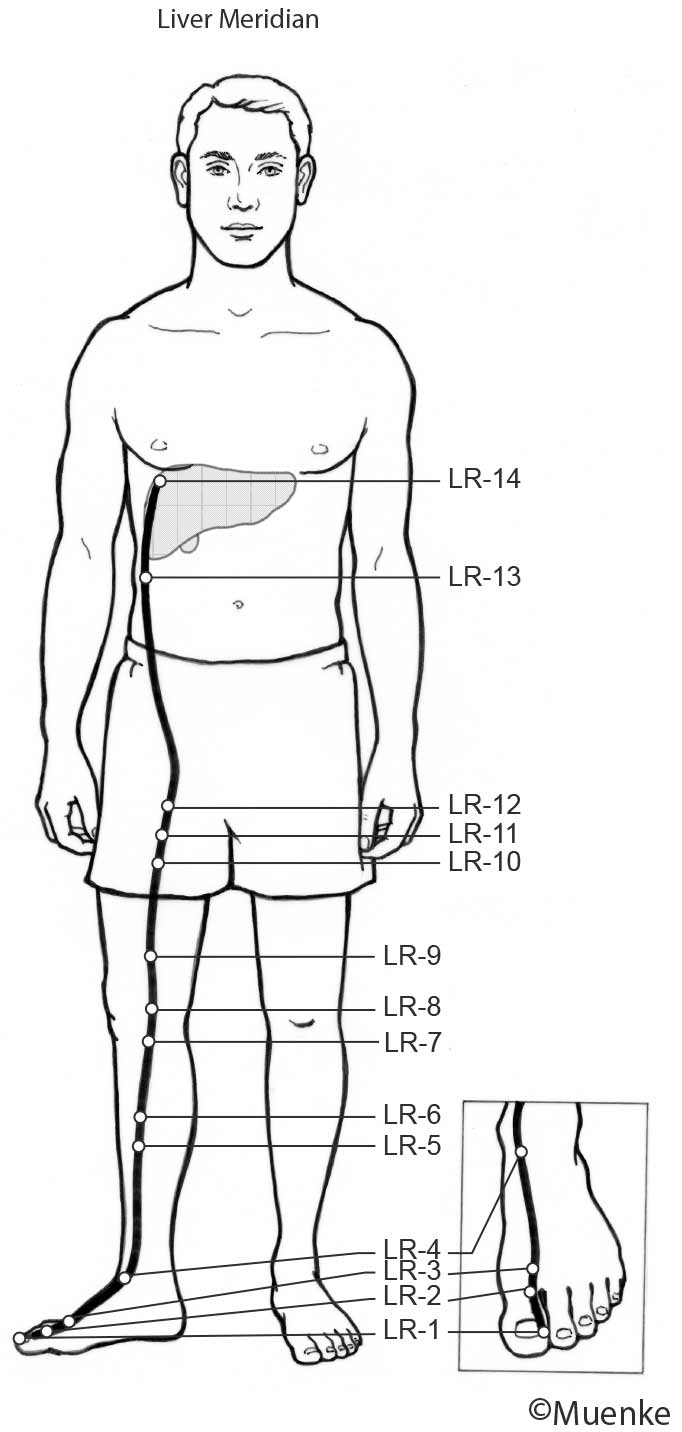
Selected Readings
- Traditional Chinese Medicine and Acupuncture
-
Joseph M. Helms: Acupuncture Energetics - A Clinical Approach for Physicians. Thieme, 1995.
Joseph M. Helms: Getting to Know YOU - A Physician Explains How Acupuncture Helps You Be The Best YOU. Random House, 2007.
Ted J Kaptchuck: The Web That Has No Weaver – Understanding Chinese Medicine. McGraw-Hill Company, 2000.
Giovanni Maciocia: The Foundations of Chinese Medicine. Churchill Livingstone, 1989.
Gabriel Stux, Brian Berman, Bruce Pomeranz: Basics of Acupuncture. 5th Edition, Springer Verlag, 2003
- Acupressure
-
Cathryn Bauer: Acupressure for Everybody - Gentle Effective Relief for more than 100 Common Ailments. Henry Holt and Company, Inc. 1991.
Michael Reed Gach: Acupressure's Potent Points - A Guide to Self-Care for Common Ailments. 1990.
Julian Kenyon: Acupressure Techniques - Well-Being and Pain Relief at your Fingertips. Inner Traditions Intl. Ltd. 1996.
- Clinical Hypnosis
-
Arreed Barabasz and John G. Watkins: Hypnotherapeutic Techniques. 2nd Edition. Taylor and Francis Books, Inc., 2005.
D. Corydon Hammond: Handbook of Hypnotic Suggestions and Metaphors. American Society of Clinical Hypnosis, 1990.
Herbert Spiegel and David Spiegel: Trance and Treatment. Clinical Uses of Hypnosis. 2nd Edition, American Psychiatric Publishing, Inc. 2004.